Over the past few centuries, we have made countless discoveries that have greatly improved the quality of our daily lives and understanding how the world around us works. Assessing the full importance of these discoveries is very difficult, if not almost impossible. But one thing is certain, some of them have literally changed our lives once and for all. From penicillin and the screw pump to X-rays and electricity, here is a list of the 25 greatest discoveries and inventions of mankind.
25. Penicillin
If the Scottish scientist Alexander Fleming had not discovered penicillin, the first antibiotic, in 1928, we would still be dying from diseases such as stomach ulcers, abscesses, streptococcal infections, scarlet fever, leptospirosis, Lyme disease and many others.
24. Mechanical watch
Photo: pixabay
There are conflicting theories about what the first mechanical watches actually looked like, but most often researchers adhere to the version that in 723 AD, the Chinese monk and mathematician Ai Xing (I-Hsing) created them. It was this fundamental invention that allowed us to measure time.
23. Heliocentrism of Copernicus
Photo: WP / wikimedia
In 1543, almost on his deathbed, the Polish astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus unveiled his landmark theory. According to the works of Copernicus, it became known that the Sun is our planetary system, and all its planets revolve around our star, each in its own orbit. Until 1543, astronomers believed that the Earth was the center of the universe.
22. Blood circulation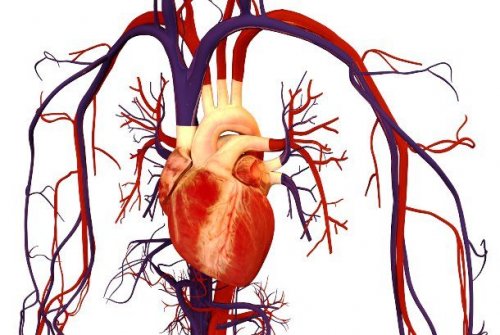
Photo: Bryan Brandenburg
One of the most important discoveries in medicine was the discovery of the circulatory system, which was announced in 1628 by the English physician William Harvey. He was the first person to describe the entire circulation system and properties of the blood that the heart pumps throughout our body from the brain to the fingertips.
21. Screw pump
Photo: David Hawgood / geographic.org.uk
One of the most famous ancient Greek scientists, Archimedes, is considered the author of one of the world's first water pumps. His device was a rotating corkscrew that pushed water up a pipe. This invention took irrigation systems to the next level and is still used today in many wastewater treatment plants.
20. Gravity
Photo: wikimedia
Everyone knows this story - Isaac Newton, the famous English mathematician and physicist, discovered gravity after an apple fell on his head in 1664. Thanks to this event, we first learned why objects fall down, and why the planets revolve around the Sun.
19. Pasteurization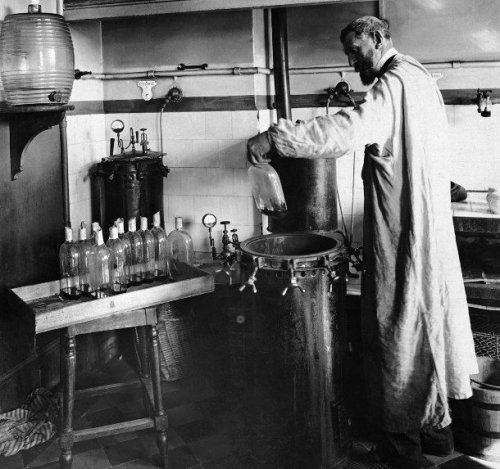
Photo: wikimedia
Pasteurization was discovered in the 1860s by the French scientist Louis Pasteur. It is a heat treatment process during which pathogenic microorganisms are destroyed in certain foods and drinks (wine, milk, beer). This discovery had a significant impact on public health and the development of the food industry around the world.
18. Steam engine
Photo: pixabay
Everyone knows that modern civilization was forged in factories built during the Industrial Revolution, and that it was all done using steam engines. The steam-powered engine was invented a long time ago, but over the past century it has been significantly improved by three British inventors: Thomas Savery, Thomas Newcomen, and the most famous of them, James Watt (Thomas Savery, Thomas Newcomen, James Watt).
17. Conditioner
Photo: Ildar Sagdejev / wikimedia
The primitive climate control system has existed since ancient times, but it changed significantly when the first modern electric air conditioner appeared in 1902. It was invented by a young engineer named Willis Carrier, a native of Buffalo, New York (Buffalo, New York).
16. Electricity
Photo: pixabay
The fateful discovery of electricity is credited to the English scientist Michael Faraday. Among his key discoveries, it is worth noting the principles of electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism and electrolysis. Faraday's experiments also led to the creation of the first generator, which became the forerunner of the huge generators that today produce the electricity we are used to in everyday life.
15. DNA
Photo: pixabay
Many believe that it was the American biologist James Watson and the English physicist Francis Crick (James Watson, Francis Crick) who discovered in the 1950s, but in fact, this macromolecule was first identified back in the late 1860s by the Swiss chemist Friedrich Meischer (Friedrich Miescher). Then, several decades after Meisher's discovery, other scientists conducted a series of studies that finally helped us figure out how an organism passes its genes to the next generation, and how its cells work.
14. Anesthesia
Photo: Wikimedia
Simple forms of anesthesia such as opium, mandrake and alcohol have been used by humans for a long time, and the first references to them date back to 70 AD. But since 1847, pain relief has been taken to a new level, when the American surgeon Henry Bigelow first introduced ether and chloroform into his practice, making extremely painful invasive procedures much more bearable.
13. Theory of relativity
Photo: Wikimedia
Incorporating Albert Einstein's two interrelated theories, special and general relativity, published in 1905, the theory of relativity transformed the entire theoretical physics and astronomy of the 20th century and eclipsed the 200-year-old theory of mechanics proposed by Newton. Einstein's theory of relativity has become the basis for much of the scientific work of modern times.
12. X-rays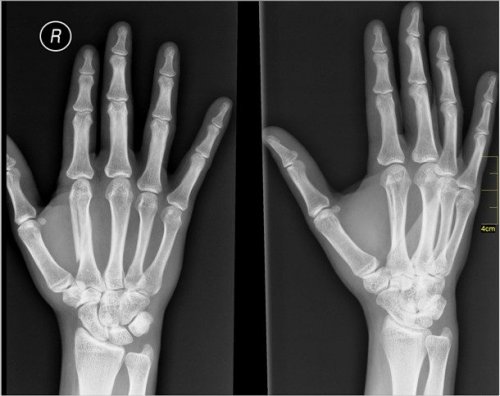
Photo: Nevit Dilmen / wikimedia
German physicist Wilhelm Conrad Rontgen accidentally discovered X-rays in 1895 when he was observing fluorescence produced by a cathode ray tube. For this landmark discovery in 1901, the scientist was awarded the Nobel Prize, the first of its kind in the field of physical sciences.
11. Telegraph
Photo: wikipedia
Since 1753, many researchers have been conducting their experiments to establish communication at a distance using electricity, but a significant breakthrough did not come until a few decades later, when in 1835 Joseph Henry and Edward Davy (Joseph Henry, Edward Davy) invented the electrical relay. With this device, they created the first telegraph 2 years later.
10. Periodic system of chemical elements
Photo: sandbh / wikimedia
In 1869, the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev noticed that if you sort chemical elements according to their atomic mass, they conditionally line up in groups with similar properties. Based on this information, he created the first periodic table, one of the greatest discoveries in chemistry, which was later nicknamed the periodic table in his honor.
9. Infrared rays
Photo: AIRS / flickr
Infrared radiation was discovered by the British astronomer William Herschel in 1800, when he was studying the heating effect of light of different colors, using a prism to spread the light into a spectrum, and measuring the changes with thermometers. Today, infrared radiation is used in many areas of our lives, including meteorology, heating systems, astronomy, tracking heat-intensive objects, and many other areas.
8. Nuclear magnetic resonance
Photo: Mj-bird / wikimedia
Today, nuclear magnetic resonance is constantly used as an extremely accurate and efficient diagnostic tool in the field of medicine. This phenomenon was first described and calculated by the American physicist Isidor Rabi in 1938 while observing molecular beams. In 1944, the American scientist was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for this discovery.
7. Moldboard plow
Photo: wikimedia
Invented in the 18th century, the mouldboard plow was the first plow that not only turned up the soil, but also stirred it up, which made it possible to cultivate even very stubborn and stony land for agricultural purposes. Without this tool, agriculture as we know it today would not exist in northern Europe or central America.
6 Camera Obscura
Photo: wikimedia
The forerunner of modern cameras and camcorders was the camera obscura (translated as dark room), which was an optical device used by artists to create quick sketches while traveling outside their studios. A hole in one of the walls of the device served to create an inverted image of what was happening outside the chamber. The picture was displayed on the screen (on the opposite wall of the dark box from the hole). These principles have been known for centuries, but in 1568 the Venetian Daniel Barbaro modified the camera obscura with converging lenses.
5. Paper
Photo: pixabay
Papyrus and amate, used by ancient Mediterranean peoples and pre-Columbian Americans, are often considered the first examples of modern paper. But it would not be entirely correct to consider them real paper. References to the first writing paper production date back to China during the Eastern Han Empire (AD 25-220). The first paper is mentioned in the annals dedicated to the activities of the judicial dignitary Cai Lun (Cai Lun).
4. Teflon
Photo: pixabay
The material that keeps your frying pan from burning was actually invented completely by accident by American chemist Roy Plunkett when he was looking for a replacement for refrigerants to make your home safer. During one of his experiments, the scientist discovered a strange slippery resin, which later became better known as Teflon.
3. The theory of evolution and natural selection
Photo: wikimedia
Inspired by his observations during his second exploratory journey in 1831-1836, Charles Darwin began to write his famous theory of evolution and natural selection, which, according to scientists from around the world, has become a key description of the mechanism of development of all life on Earth.
2. Liquid crystals
Photo: William Hook / flickr
If the Austrian botanist and physiologist Friedrich Reinitzer had not discovered liquid crystals while testing the physico-chemical properties of various cholesterol derivatives in 1888, today you would not know what LCD TVs or flat LCD monitors are.
1. Polio vaccine
Photo: GDC Global / flickr
On March 26, 1953, American medical researcher Jonas Salk announced that he had successfully tested a vaccine against polio, a virus that causes severe chronic illness. In 1952, an epidemic of this disease diagnosed 58,000 people in the United States, and the disease claimed 3,000 innocent lives. This spurred Salk to seek salvation, and now the civilized world is safe at least from this disaster.
As children, we told each other horror stories, frightening with vampires, zombies, demons, ghosts... However, sometimes reality can be stranger and creepier than fiction, even in such a serious area as science. We offer you a selection the most terrible scientific discoveries and phenomena.
space madness
In recent years, there has been a lot of talk about flights to Mars and even its colonization, arguing that it will begin in 2030. However, a recent study led to frightening conclusions. Lab mice were exposed to charged particles similar to those from which astronauts - the conquerors of the Red Planet - would not be protected in deep space.
Exposure to these particles led to inflammation in the rodents' brains, causing loss of cognition and a state of constant anxiety.
This "cosmic madness" did not pass even six months after the irradiation.
At present, there is no method of completely protecting astronauts from the effects of cosmic radiation, so it is possible that a terrible fate awaits the future conquerors of Mars.
DNA theft
Now, thanks to its poisonous properties, it is able to instantly dissolve cell membranes and freely penetrate inside in order to begin to multiply rapidly.
The authors of the study argue that this is a completely unique case - until now it was believed that viruses “steal” genes only from bacteria, and not from multicellular creatures. It is not known how many such viruses exist and whose properties they are able to assign.
Salton Sea Fault
For years, seismologists have argued that the famous San Andreas Fault in the United States is long overdue for a terrible earthquake of magnitude eight or higher on the Richter scale.
However, a reason has recently been found why the catastrophe has not yet occurred. It turned out that there is another fault parallel to San Andreas under the Salton Sea Lake, which, perhaps, keeps the tectonic plate from destruction, "pulling" tension in the earth's crust onto itself.

The discovery caused a complete reassessment of the seismic hazard for the region in which Los Angeles is located. While the Salton Sea Fault serves to ease stress on San Andreas for the time being, its presence doubles the risk of destruction to the US West Coast in the event of a major disaster.
Killer car
Artificial intelligence is undoubtedly one of the most important technologies of the near future. However, researchers at the American Carnegie Mellon University have recently shown that he can be very violent. They created an artificial neural network that can kill anyone and everyone. True, they did it in the virtual world, namely in the popular online game Doom.
The artificial intelligence learned to play by receiving “rewards” for killing from the creators, and soon began to defeat all human players. For now, he just plays computer games, but who knows what will happen tomorrow...
caroline butcher
Paleontologists at North Carolina State University recently discovered an animal species unknown to science that is older than dinosaurs and ancient crocodiles. Despite the fact that this eerie creature has been extinct for over 200 million years, the knowledge that it once roamed the planet can bring shivers and nightmares.
Reconstruction of Carnufex carolinensis

They named this monster Carnufex carolinensis ("Caroline butcher") - an appropriate name for a crocodile-like creature about three meters high, which walked on two legs like a man.
This animal lived on land and had terrible teeth, similar to the blades of a huge blade. This creature was probably the most dangerous predator before the advent of dinosaurs.
Worm Buddy
US biology professor Jonathan Allen once felt in 2012 that he had a strangely coarsened patch of skin on his face. The most frightening thing was that this area began to move across the face. Once, when the professor was taking exams, the stain moved to his mouth, and a small worm began to be visible in it.
The same worm with the scientific name Gongylonema pulchrum (left). He is in the lip of another patient (on the right)

It turned out to be a rare worm that infected only 13 people in the United States, including the professor himself. The case ended with the fact that Jonathan Allen published an article about his intruder, whom he named Buddy.
Terrible Jupiter Soundtrack
NASA's Juno spacecraft was tasked with collecting data on Jupiter, the mysterious gas giant. Flying over the planet, "Juno" collected information about the planet's radio emissions.
Engineers on Earth then decoded the data received by the craft into sound files. And they were shocked by the result - from the depths of space, it was as if they heard music written for a horror movie, with screeching sounds that resemble frightened human voices. Scientists hope to find out the nature of these sounds.
The ghost behind
Sometimes, for no reason at all, we begin to feel like we are being watched. Even if you know that there is no one around, this feeling does not disappear and is very unnerving.
Such an experiment was recently carried out. The person was asked to randomly wave their arms. At the same time, behind him was a robot that repeated all the movements of a person.
While the movements coincided, the subject did not feel anything special. But when the movements of the robot ceased to be synchronous with the movements made by the participants in the experiment, it began to seem to people that something terrible was standing behind them. They were so horrified that they asked to stop the experiment.
spider zombie
It turns out that the female wasp lays an egg in the abdomen of the spider. The larva that has matured in the spider body feeds on its blood, in response releasing a substance into the carrier, which, acting on the nervous system of the arthropod, makes it a thoughtless builder of a strong wasp nest. After the work is completed, the larva devours its zombie slave, and then settles in a cocoon built by him.
Matthew's face
Hurricane Matthew raged this fall and resulted in catastrophic destruction and numerous loss of life. The people of Haiti, already exhausted by poverty, took the brunt of it - not only buildings were destroyed on the island, but more than 1000 people died.
In an infrared image of the hurricane taken from the NASA weather satellite on October 4, we see that it looks very much like a skull with an eye, which was the center of the hurricane.

According to one version, the Nobel Prize fund was formed because Alfred Nobel wanted his name to be associated with him, and not with the dynamite he invented. Throughout the history of mankind, many scientists regretted their discoveries, and some simply did not understand that their inventions were dangerous for both the environment and humans. Let's look at a list of 15 dangerous inventions. We formed it on the basis of the opinion of the majority, if it were based on the subjective opinion of the author, then a few more points would be added, for example, serial films and Coca-Cola. So, about the serious.
No one will be surprised that we started our list with nuclear weapons. World countries that have not abandoned it use it as a way to intimidate opponents. However, if one day several countries decide to apply it simultaneously, then the worst of the scenarios is the split of the planet (and this is not a figurative expression), the best is a climate catastrophe, the destruction of the ozone layer, the death of all life.

The next item is nuclear technology again. How often have we heard about the peaceful atom, about how cheap nuclear energy is for us, and that with well-established operation, nuclear power plants do not harm the environment. But who can guarantee their smooth operation?
The consequences of the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant, which occurred in 1986, are still felt. Another problem is the radioactive waste that we pass on to our descendants by inheritance.

Another weapon of mass destruction, involving the use of the toxic properties of certain substances that produce a poisonous effect. How disastrous this is, we know from the history textbook (used during world wars) and from news stories (modern civil wars).

In the 40s of the twentieth century, the development of chemical fertilizers appeared, after a few decades their mass production began. Of course, this is an effective and quick way to increase the amount of food that is constantly in short supply for the entire population of the planet.
But phosphorus, nitrogen and other fertilizers harm flora, fauna, incl. adversely affect human health, contribute to the occurrence of serious diseases.

Another chemical that helps increase yields while preserving them are pesticides used to control pests, weeds, plant diseases. They harm the ecosystem as a whole, in particular they cause great damage to birds. A person can cause allergic reactions, diathesis.

Everyone knows what harm internal combustion engines do to us. Thanks to them, the excess concentration of heavy metals in the air. On the conscience of the inventor of such an engine and the destruction of the ozone layer.

Since we are talking about the thinning of the ozone layer, then how can we not recall the freon invented in 1928. This gas was used for a long time in refrigeration equipment, perfumery, before they realized how dangerous it was for the environment.

And again, hunger gave rise to a new discovery - genetically modified foods that are more resistant to external influences. However, many scientists agree that this is a "time bomb", the consequences of their use can be serious diseases, mutations.

The problem is not in the technology itself, but in the fact that again it is impossible to exclude accidents, the consequences of which for the environment are catastrophic. For example, in 1978, as a result of an accident on an American tanker, 220 thousand tons of oil were spilled, and the ecology in that area has not recovered to this day.

toxic fluorine, nitrogen and carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide- all these are by-products of obtaining aluminum by electrolysis. These toxic substances adversely affect vegetation (especially fluorine) and human health (bronchitis and other respiratory diseases develop).

When burned, polyethylene waste emits a toxic substance, and does not decompose in the soil, but contributes to the reproduction of harmful organisms. Draw your own conclusions.

You can’t call antibiotics harmful, in many respects we owe our considerable life expectancy precisely to the discovery of penicillin. The dangerous thing is that they are sold without a prescription, and most consider them a magic pill for everything. In practice, they poison the entire body, harm the functioning of the liver and kidneys. Using them inappropriately can lead to negative consequences.

Let's comment on the last three points in a general way. Entrepreneurial people build their super-profitable business on human weaknesses. Someone is trying to escape from reality, causing irreparable harm to their body and replenishing the wallets of others. There is no need to say anything more when so much has already been written about it. Warnings are posted even on cigarette packaging, it's too bad that not everyone takes them seriously.
“When you are doing science, you do not know how the fruits of your creativity will be used. Any discovery is neutral from a moral point of view. People can use it for both good and destructive purposes. It's not science's fault," Galston told The New York Times.
Mikhail Kalashnikov: AK-47
All Kalashnikov wanted was to protect his country. With this thought, he went to military service. More than once, the future inventor had to hear the complaints of his comrades about the unreliable and dangerous to use rifles that were in service with the Soviet Army. Combining an interest in weapons and engineering talent, Kalashnikov created his main brainchild - an assault rifle, called the AK-47.
“This is the most popular and effective firearm in the world. Its design is so simple that in many countries the machine costs less than a live chicken.
The Kalashnikov assault rifle is cheap to manufacture, lightweight, durable and suitable for use in any climatic conditions. Having been awarded the title of Hero of Russia, Kalashnikov was proud of his services to the country all his life.
Unfortunately, many terrorist groups have established homemade production of AK-47s. The fall of weapons into the service of criminals upset the inventor.
“I am proud of my invention, but I am sad that terrorists use it. If I had a choice, I would prefer to invent some useful device for farmers, for example, a lawn mower,” Kalashnikov told The Guardian.
Of the 100 million AK-47s produced by 2009, half were made underground. The creator of the automaton was so depressed by this fact that he wrote a letter to the head of the Russian Orthodox Church.
“My heartache is unbearable. I am tormented by the question: if my rifle kills people, am I responsible for their death? Kalashnikov asked the Patriarch.
The church removed the blame from the inventor and thanked him for his service, and six months later Kalashnikov died.
Orville Wright: airplane
Everyone has heard about how Orville and Wilbur Wright invented and built the first airplane and then took it into the air. Having advocated the use of aviation for peaceful purposes all their lives, the Wrights did not expect to see their creations being used as weapons.
The brothers sold aircraft to the US Army, but believed that the winged vehicles would only be used by the military to monitor the enemy. As a World War I survivor, Orville realized the devastation that military aviation can bring.
"The airplane has made the war so terrible that I do not believe that any country will want to start a conflict again," he wrote to the Aviation Industry Council.
“The aircraft, which made the possibilities of destruction limitless, actually became a guarantee of peace,” said Orville Wright, speaking on radio five years later.
However, after seeing the consequences of air bombing during World War II, Wright finally realized that aviation only increased the death toll and regretted his invention.
“We wanted to create something that will ensure peace on Earth. But we were wrong,” Wright said in a suicide interview.
Robert Oppenheimer: The Atomic Bomb
It is well known that Einstein regretted his part in the creation of the atomic bomb. However, the theoretical physicist was not directly involved in the design and construction of super-powerful weapons.
During World War II, another scientist, Julius Robert Oppenheimer, realized that the creation of an atomic bomb could put an end to military confrontation. While working at the Los Alamos Laboratory, Oppenheimer studied the chain reactions of fast neutrons necessary for an atomic explosion.
Realizing how terrible the power of nuclear weapons, Oppenheimer began to insist on the introduction of international control over the use of atomic energy. As a result, the physicist was appointed chairman of the General Advisory Committee of the Atomic Energy Commission.
Oppenheimer strongly protested against the production of more and more atomic bombs, but because of the scientist's contacts with the communists, the government doubted his trustworthiness. As a result, Oppenheimer had to curtail his anti-nuclear agitation. The use of atomic bombs and the threat of nuclear war oppressed the scientist until the end of his days.
We offer a selection of interesting scientific discoveries of recent times.
See death. This month, British scientists made an interesting discovery: they captured on camera the spread of death. The process itself was a blue glow that, in the literal sense of the word, permeated the cells of the body while it was dying. The very goal pursued by scientists from the Research Council for Biotechnology and Biological Sciences was to deepen knowledge in the processes of death in order to further try to increase human life expectancy. (According to the Daily Mail. Photo: DailyMail)

Ancient Mayan temple. Archaeologists discovered an ancient temple in the jungles of Guatemala last year. Presumably, this temple belonged to the Mayan tribes 1600 years ago and was called the “Temple of the Night Sun”. The temple itself is adorned with gigantic masks of the Mayan solar god.

New animal species in Peru. Between 2009 and 2012, a group of biologists from Mexico and Peru traveled in search of new animal species to the northern part of Peru, the Tabaconas Namballe National Reserve. During the entire expedition, they discovered many new species of mammals. Among them is an unknown species of night monkey. Only last year, scientists managed to agree that this species of monkeys was really not known to science. Disputes over some other species of mammals are still ongoing. (according to nationalgeographic.com, photo: National Geographic)


Solar systems and planets. In April 2012, scientists discovered an interesting star in the constellation South Hydra. The Sun-like star is 127 light-years from Earth. At least 9 planets revolve around it, which makes this solar system the largest known. Our solar system has only 8 official planets. (according to nationalgeographic.com, photo: National Geographic)

Baby teeth and dictators. Scientists have made an interesting conclusion why, most likely, dictators are born. Approximately 1 in 2000 babies are born with one erupted tooth. For a mother, feeding such a child turns into real torment. The child feels a lack of attention, and with age, subconsciously tries to win it more and more. Anthropologists claim that people like Julius Caesar, Hannibal, Napoleon, Mussolini, and Hitler were born with an erupted tooth. (according to www.mentalfloss.com, photo: open sources)

Tie and vision. After many years of research, American scientists came to the conclusion that in 67% of men, visual impairment is associated with a tightly tightened collar. This is especially true for those who wear a tie. A tight tie restricts blood flow to the eyes. It also affects blood pressure. (according to Stephen Juan, "The odd body", photo: public sources)


Chimpanzee and deceit. The conclusion was made by zoologists from Sweden. They found that a chimpanzee named Santino, who constantly threw stones at zoo visitors, prepared the weapon in advance. Santino has been under surveillance for a long time. Without giving a look, he waited for the visitors to reach a certain place, and then quickly took out and threw a stone. Scientists concluded that such an action is the result of a well-thought-out plan, which means that chimpanzees are capable of deceit. (according to the journal PLoS ONE and the ScienceNOW website, a photo: open sources )

happiness and food. British scientists came to the conclusion that only food can bring true happiness to a person. Everyone knows that a hungry person often has a bad mood, but as soon as he eats, his mood improves. In the first place among the “products of happiness” were all kinds of sweets and french fries - for most people, these products are associated with relaxation. Next on the list are red and black caviar. It is associated with wealth and luxury. (according to www.geo.ru, a photo: open sources)

Mars and water NASA experts have come to the final conclusion that in the distant past there was water on the red planet suitable for living organisms. They managed to make such a conclusion with the help of the Opportunity rover. The spacecraft found a piece of ancient clay that could only form in the presence of water. (according to bbc.co.uk, photo: NASA)
