Individual entrepreneur(IP)- registered in statutory order and carrying out entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity.
To acquire the status of an individual entrepreneur, a citizen must have the following common features subject of civil law:
Legal capacity (the ability to have civil rights and bear obligations);
Legal capacity (the ability to acquire and exercise civil rights by one's actions). Only capable citizens can carry out entrepreneurial activities, that is, those who are able to independently perform legal actions, conclude transactions and execute them, acquire property and own, use and dispose of it. By general rule civil capacity arises in full from the onset of adulthood (upon reaching 18 years of age);
Have a place of residence (a place where a citizen lives permanently or predominantly).
The status of an individual entrepreneur is acquired as a result of state registration citizen as an individual entrepreneur.
A citizen has the right to engage in entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity from the moment of state registration as an individual entrepreneur, and state registration can only be carried out at the place of his official permanent registration at the place of residence.
To register an entrepreneur, you must prepare the following documents:
a copy of the passport and certificate with the TIN number;
receipt of payment of the fee;
an application for registration of an individual entrepreneur of a certain sample in two copies.
Citizens registered as individual entrepreneurs have rights and obligations.
IP rights:
Ability to choose the types of activities permitted by law.
The right to hire workers.
Freedom to choose partners and products. The entrepreneur himself determines the market segment in which he will develop his business.
The right to independently determine the cost of goods and services offered.
The individual entrepreneur himself decides how and how much to pay his employees.
The entrepreneur has the right to dispose of the profits as he pleases.
An individual entrepreneur has the right to appear in court as a plaintiff and a defendant.
An individual entrepreneur is a business entity that also has certain responsibilities. Namely:
All individual entrepreneurs are required to adhere to the norms of the current legislation.
All cash transactions are documented. Such documents include, a contract for the supply of goods, etc.
To carry out licensed types of business, an entrepreneur must obtain a state permit - a certificate, patent or license.
All employees who are hired by an individual entrepreneur must be officially registered. That is, the IP concludes with a person labor contract, an agreement on the performance of specific works or other agreements. After completing the documents, the entrepreneur is obliged to make the necessary contributions to the Medical Insurance Fund, the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund.
If the activity of the IP causes harm environment, he is obliged to take measures to reduce negative impacts. If a businessman cannot resolve this issue on his own, he must contact the environmental service.
The entrepreneur is obliged to pay taxes to the state treasury in a timely manner.
An individual entrepreneur is a participant in market relations who must always respect the rights of the buyer.
If, for some reason, the IP has changed data (surname, place of registration or residence, type of activity), he is obliged to notify the relevant authorities - the tax office, funds and other institutions.
An individual entrepreneur is obliged to pay a fixed payment to social funds, regardless of income.
There are four taxation systems:
Ordinary system of taxation (OSNO);
Simplified taxation system (USNO);
Single tax on imputed income (UTII);
Patent taxation system (PSN).
The status of an individual entrepreneur has the following advantages compared to registering your own enterprise:
simplification of the processes of creating and liquidating a business;
free use of own proceeds;
Individual entrepreneur (IP): details for an accountant
Circumstances: an individual entrepreneur who has already been brought to administrative responsibility is brought to administrative responsibility ... that the contested legal provision applies to an individual entrepreneur who acts as an insured in relation to ..., if such an obligation is not fulfilled by an individual entrepreneur, it becomes possible to interpret, assuming, .. .one imperfection of the current legislation: now individual entrepreneurs will not be held accountable...
Entrepreneurial activity. On the contrary, if an individual entrepreneur carries out activities outside the scope of types ... information about an individual entrepreneur contained in the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs. Non-submission (... the totality of the above norms implies that an individual entrepreneur initially has a common (universal) ... 1. The nature of the operation. For example, an individual entrepreneur carries out retail trade in food products ...
How to calculate insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs in 2017? Individual entrepreneurs using the USNO with ... are distributed. The revolutionary decision of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation An individual entrepreneur applying the simplified taxation system with an object ... to the court of first instance. The position of an individual entrepreneur. The sole proprietor argues that it is unlawful to calculate ... the contributions payable by the sole proprietor for himself. But an individual entrepreneur turned to the RF Armed Forces ...
Exceeded by an individual entrepreneur during the reporting (tax) period, such an individual entrepreneur, according to ... determination of the residual value of fixed assets by individual entrepreneurs, is carried out according to the rules established by ... accounting "is not applicable to individual entrepreneurs. Firstly, individual entrepreneurs applying the simplified tax system, on ... the basis of the implementation of entrepreneurial activities by individual entrepreneurs and organizations, manifest themselves and ...
Year. This case affects all individual entrepreneurs applying the simplified taxation system, since it is fundamentally ... compulsory pension insurance payable by an individual entrepreneur who pays personal income tax and does not produce ... paid for compulsory pension insurance by individual entrepreneurs for themselves, the base must be calculated ... insurance premiums paid to the FIU. Individual entrepreneurs applying the USNO with the object of taxation ...
The cost criterion for the depreciable property of individual entrepreneurs applying the general taxation system ... the cost criterion for the depreciable property of individual entrepreneurs applying the general taxation system ... b) the property must be directly used by the individual entrepreneur to carry out entrepreneurial activities; in ... the element of taxation - the procedure for calculating income tax by individual entrepreneurs - are subject to ...
Most cases. Initially, it seems that it is indeed easier to be an individual entrepreneur. Legal ... in any form regulated by law. It is not at all necessary for an individual entrepreneur to open a separate ... implying the distribution of certain standards for individual entrepreneurs. Continuation
Not only legal entities and individual entrepreneurs (IP), but also individuals... concluding a contract with an individual, except for an individual entrepreneur or another engaged in private practice ... The named individuals do not have the status of an individual entrepreneur, but in accordance with the tax ... agreement with a legal entity or an individual entrepreneur. However, as mentioned above...
Federation of goods by bodies, organizations or individual entrepreneurs authorized to carry out such implementation, ... established organizations or newly registered individual entrepreneurs, within a given three-month period ... to the state, provided by a foreign person to a Russian individual entrepreneur, the territory is recognized Russian Federation... texts provided by foreign organizations to a Russian individual entrepreneur, then, since the place of sale ...
Patronymic - for an individual entrepreneur; taxpayer identification number assigned to the organization (individual entrepreneur) that issued (issued) the document ... -FZ. According to it, individual entrepreneurs using PSNO, with the exception of individual entrepreneurs engaged in types of entrepreneurial ... sale without forming a legal entity, individual entrepreneurs recognized as agricultural producers). Retail...
Categories of taxpayers, including individual entrepreneurs, lawyers, notaries, other persons, ... number of lines 051 and 052. Individual entrepreneurs. Individual entrepreneurs are required to submit a tax return based on... payment documents) common mode taxation should...
Whether they are self-employed or not. Payment by the individual entrepreneur of insurance premiums is carried out ... insurance from an individual entrepreneur arises from the moment of acquiring the status of an individual entrepreneur and until ... extra-budgetary funds by an individual entrepreneur are made from the moment of acquiring the status of an individual entrepreneur and up to ... 49921 The amount of remuneration paid by an individual entrepreneur to his employees for non-disclosure...
Federation of goods by bodies, organizations or individual entrepreneurs authorized to carry out such sale, tax ... by a person of entrepreneurial activity as an individual entrepreneur, a real estate object that remains in ... under a donation agreement, then the transfer by an individual entrepreneur recognized as a VAT taxpayer of the said property. .. do not apply to organizations and individual entrepreneurs trading in excisable goods. AT...
The moment of state registration as an individual entrepreneur. State registration of IP is regulated federal law... The taxpayer, when registering as an individual entrepreneur, independently indicates the types economic activity... (not only organizations) that makes payments to an individual entrepreneur. He needs to track (apparently ... and the preparation of statistical information. This means that an individual entrepreneur has the right to engage in any type of activity ...
The activities of an individual as an individual entrepreneur are calculated, withheld and listed in ... Article 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), and an individual entrepreneur engaged in entrepreneurial activities, who is obliged ... to whether they are individual entrepreneurs or not. Payment by the individual entrepreneur of insurance premiums is carried out ... premises, dachas, land plots, owned by an individual entrepreneur on the right of ownership, is valid only ...
I think many of the readers have come across the abbreviation "IP", as well as "PBOYuL" or "PE", or simply the words "merchant", "entrepreneur", or the most famous - "businessman". And what do they, in essence, mean? It is worth looking into the law.
As such, there is no special law on IP and is not expected. IP is dedicated, which says that a citizen has the right to engage in entrepreneurial activity at his own peril and risk without creating.
In essence, nothing changes in a person - having received the status of an individual entrepreneur, he does not become a brilliant “business shark”. It’s just that in the corresponding state register (EGRIP) an entry appears stating that such and such a citizen of such and such a number is registered in the status of an individual entrepreneur. The state needs this, first of all, to levy taxes from this citizen, which he is obliged to pay, making a profit from entrepreneurial activities.
Read also: Registration of an individual entrepreneur of a foreign citizen or how to open an individual entrepreneur by temporary registration in 2019
Many people mistakenly consider an individual entrepreneur to be a legal entity, and often such stupid questions arise as: “buy a ready-made IP” or “”. A citizen, having received the status of an individual entrepreneur, remains an individual and, of course, it is impossible to buy or divide it.
The fact of its state registration (still the same article 23 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Since Certificates are no longer issued during registration, and the Record Sheet still does not look very solid, it is easier to indicate in the contract that the individual entrepreneur acts on the basis of state registration from such and such a date , OGRNIP such and such.
The same as for "ordinary" citizens, plus the right to engage in entrepreneurial activities. But there are a few more responsibilities, among them:
You can voluntarily refuse the status of an individual entrepreneur, or you can lose it. Among the reasons:
After the amendments in 2015, and the emergence of a full-fledged institution of bankruptcy of citizens, the bankruptcy of an individual entrepreneur, in fact, became equated to the bankruptcy of a citizen, while observing the features of this type of bankruptcy.
Features of the bankruptcy of IP are regulated by articles 214-216 of the Federal Law "On insolvency (bankruptcy)", and are:
To the sign of insolvency, in addition to the inability to satisfy the requirements of creditors, the inability to repay current payments was added (Article 214 of the Federal Law and Law);
The consequences of bankruptcy for IP will be as follows:
Individual Entrepreneur (IP)(obsolete private entrepreneur (PE), PBOYuL until 2005) is an individual registered as an entrepreneur without forming a legal entity, but in fact having many of the rights of legal entities. For individual entrepreneurs, the rules of the civil code governing the activities of legal entities are applied, except when separate articles of laws or legal acts are prescribed for entrepreneurs. ()
Due to some legal limitations (it is impossible to appoint full-fledged directors to branches in the first place), an individual entrepreneur is almost always a micro-business or small business.
Fine from 500 to 2000 rubles
In case of gross violations or when working without a license - up to 8,000 rubles. And, possible suspension of activities up to 90 days.
From 0.9 million rubles for three years, and at the same time the amount of arrears exceeds 10 percent of the tax payable;
From 2.7 million rubles
Fine from 100 thousand to 300 thousand rubles. or in the amount of the culprit's salary for 1-2 years;
Forced labor for up to 2 years);
Arrest for up to 6 months;
Imprisonment for up to 1 year
If the individual entrepreneur fully pays the amount of arrears (taxes) and penalties, as well as the amount of the fine, then he is exempt from criminal prosecution (but only if this is his first such charge) (Article 198, clause 3. of the Criminal Code)
Tax evasion (fees) in particular large size(Art. 198 para. 2 (b) CC)
From 4.5 million rubles for three years, and at the same time, the amount of arrears exceeds 20 percent of the tax payable;
From 30.5 million rubles
Fine from 200 thousand to 500 thousand rubles. or in the amount of the culprit's salary for 1.5-3 years;
Forced labor for up to 3 years;
Imprisonment for up to 3 years
If the amounts for criminal prosecution are not reached, then there will only be a fine.
Non-payment or incomplete payment of tax (fee) amounts
1. Non-payment or incomplete payment of tax (fee) as a result of understatement of the tax base, other incorrect calculation of the tax (fee) or other unlawful actions (inaction) shall entail the collection of a fine in the amount of 20 percent of the unpaid amount of the tax (fee).
3. The acts provided for by paragraph 1 of this article, committed intentionally, entail the collection of a fine in the amount of 40 percent of the unpaid amount of the tax (fee). (Article 122 of the Tax Code)
If you are only late in paying (but not providing false information), then there will be penalties.
Penalties are the same for everyone (1/300 multiplied by the key rate of the Central Bank per day of the amount of non-payment) and are now somewhere around 10% per annum (which is not very much in my opinion, given that banks give loans at least at 17-20 %). You can count them.
Some types of activities an individual entrepreneur can only engage in after obtaining a license or permissions. The licensed activities of individual entrepreneurs include: pharmaceutical, private detective, transportation of goods and passengers by rail, sea, air, and others.
An individual entrepreneur cannot engage in closed activities. Such activities include the development and / or sale of military products, the circulation of narcotic drugs, poisons, etc. Since 2006, the production and sale of alcoholic beverages have also been banned. An individual entrepreneur cannot be engaged in: the production of alcohol, wholesale and retail alcohol (excluding beer and beer-containing products); insurance (i.e. being an insurer); banking activities, investment funds, NPF and pawnshops; tour operator activity (travel agent can); production and repair of aviation and military equipment, ammunition, pyrotechnics; production of medicines (realization is possible) and some others.
It is legally impossible to appoint a director in a sole proprietorship. The sole proprietor will always be the main manager. However, it is possible to issue a power of attorney to conclude transactions (clause 1, article 182 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Since July 1, 2014, for individual entrepreneurs, it has been legally possible to transfer the right to sign an invoice to third parties. Declarations could always be submitted through representatives.
All this, however, does not make the people to whom some powers are delegated directors. For directors of organizations, a large the legislative framework about rights and obligations. In the case of an individual entrepreneur, one way or another, he himself is responsible under the contract, with all his property and he himself is responsible for any other actions of third parties by proxy. Therefore, issuing such powers of attorney is risky.
State registration of an individual entrepreneur carried out by the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation. The entrepreneur is registered with the regional tax office at the place of registration, in Moscow - MI FTS RF No. 46 for Moscow.
Sole proprietors can be
OKVED codes for an individual entrepreneur are the same as for legal entities
Required documents for registration of an individual entrepreneur:
An application for registration of an individual entrepreneur and other documents can be prepared online in a free service.
Within 5 days you will be registered as an individual entrepreneur or you will receive a refusal.
You must provide documents:
1) Certificate of state registration of an individual as an individual entrepreneur (OGRN IP)
2) Extract from a single state register individual entrepreneurs (EGRIP)
After IP registration it is imperative to register with the pension fund and the Compulsory Health Insurance Fund, and obtain statistics codes.
Also necessary, but optional for an entrepreneur, is opening a current account, making a seal, registering a cash register, registering with Rospotrebnadzor.

IP pays a fixed fee to the pension fund for the year, 2019 - 36,238 rubles + 1% of income over 300,000 rubles, 2018 - 32,385 rubles + 1% of income over 300,000 rubles. A fixed contribution is paid regardless of income, even at zero income. To calculate the amount, use the IP fixed payment calculator. In the same place, the CSC and the details of the calculus.
An individual entrepreneur can apply tax schemes: STS (simplified), UTII (imputation) or PSN (patent). The first three are called special modes and are used in 90% of cases, because. they are preferential and simpler. The transition to any regime occurs voluntarily, upon application, if you do not write applications, then the OSNO (general taxation system) will remain by default.
Taxation of an individual entrepreneur almost the same as for legal entities, but instead of income tax, personal income tax is paid (with OSNO). Another difference is that only entrepreneurs can apply PSN. Also, IP does not pay 13% of personal profit in the form of a dividend.
The entrepreneur has never been obliged to keep accounting records (chart of accounts, etc.) and submit accounting reports (only the balance sheet and income statement apply to it). This does not exclude the obligation to keep tax records: declarations of the USN, 3-NDFL, UTII, KUDIR, etc.
An application for the simplified tax system and other documents can be prepared online in a free service.
Of the inexpensive programs for individual entrepreneurs, one can single out with the possibility of submitting reports via the Internet. 500 rubles / month. Its main advantage is ease of use and automation of all processes.
It is more difficult to get a loan from a bank for an IP business than a legal entity. Many banks also give mortgages with tension or require guarantors.
If a business loan is denied, then you can try to take out a consumer loan as an individual, without even disclosing plans to spend money. Consumer loans usually have high rates, but not always. Especially if the client can provide a deposit or he has a salary card in this bank.
In our country, hundreds of funds (state and not only) provide advice, subsidies, soft loans for individual entrepreneurs. AT different regions- different programs and help centers (you need to look). .
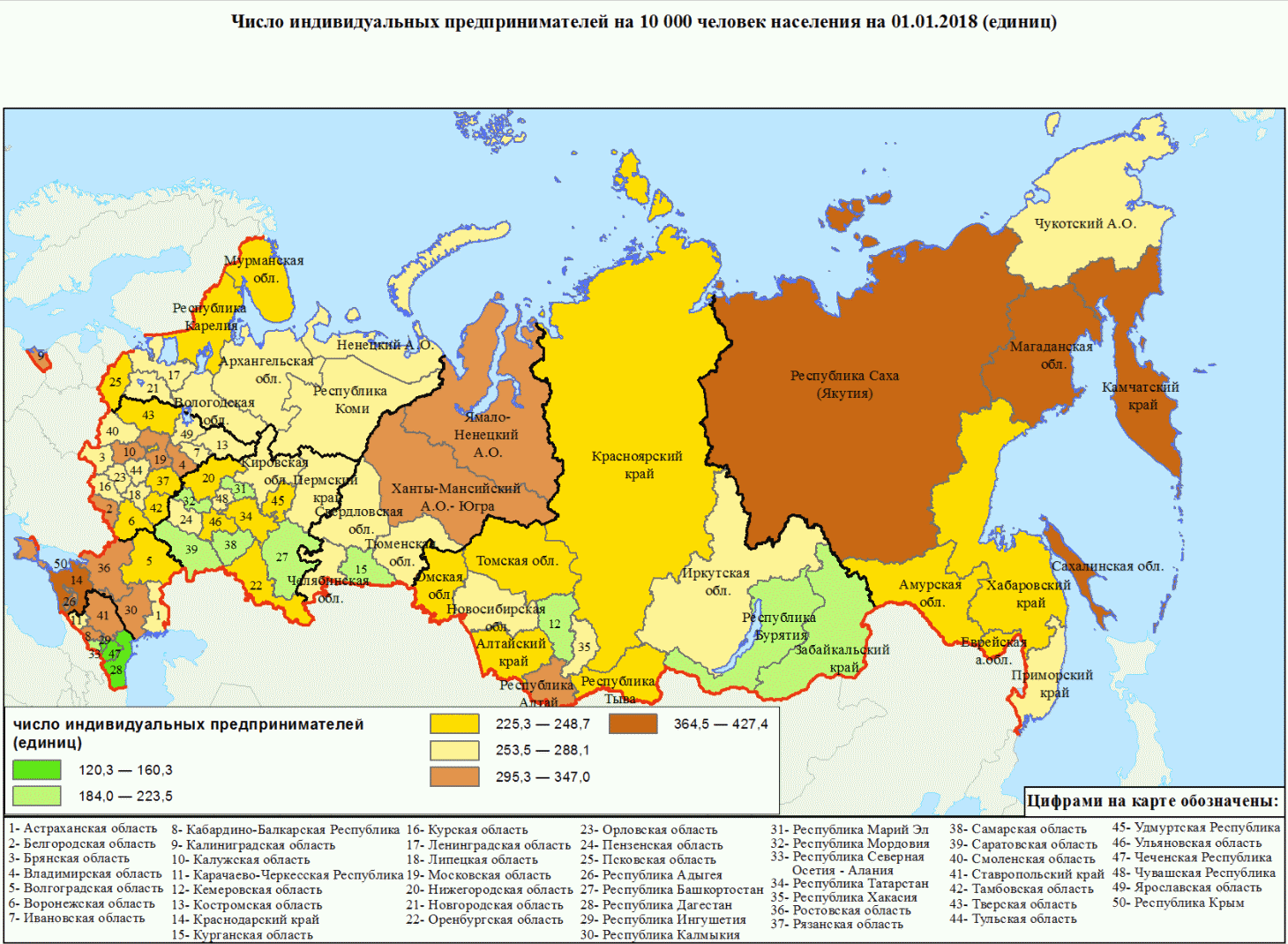

Rice. Number of individual entrepreneurs per 10,000 population
If the entrepreneur regularly pays everything to the FIU, then the pension period goes from the moment of state registration until the closure of the IP, regardless of income.
By current legislation An individual entrepreneur will receive a minimum pension, regardless of how much he pays to the FIU.
The country is undergoing an almost continuous pension reform, and therefore it is not possible to accurately determine the size of the pension.
Since 2016, if a pensioner has the status of an individual entrepreneur, then he will not have pension indexation.
The insurance period for the FSS goes only if the entrepreneur voluntarily pays social insurance contributions (FSS).
Labor Code does not apply to IP. It is accepted only for employees. IP, unlike the director, does not apply to mercenaries.
Theoretically, an individual entrepreneur can hire himself, assign a salary and make an entry in the work book. In this case, he will have all the rights of an employee. But it is not recommended to do this, because. Then you have to pay all payroll taxes.
Maternity can only be received by a woman entrepreneur and only on condition of voluntary insurance in social insurance. .
Allowance up to one and a half can be received by any businessman, regardless of gender. Either in RUSZN or in the FSS.
IP leave is not allowed. Because he has no concept of working time or rest time, and the production calendar does not apply to him either.
Sick leave is only for those who are voluntarily insured with the FSS. Calculation based on the minimum wage, the amount is insignificant, therefore, in social insurance, it makes sense to insure only mothers for maternity.
Liquidation of an individual entrepreneur is an incorrect term. An entrepreneur cannot be liquidated without violating the Criminal Code.
IP closing happens in the following cases:
Partially free Contour.Focus The most convenient search. It is enough to enter any number, surname, name. Only here you can find OKPO and even accounting information. Some information is hidden.
Is free Federal Tax Service database EGRIP information (OGRNIP, OKVED, PFR number, etc.). Search by: OGRNIP / TIN or full name and region of residence (patronymic name is not required).
Is free FSSP Learn about enforcement proceedings for the collection of debts, etc.
With the help, you can keep tax records on the simplified tax system and UTII, generate payments, 4-FSS, Unified settlement, SZV-M, submit any reports via the Internet, etc. (from 325 r / month). 30 days free. On first payment. For newly created IPs now (free of charge).
Can I register on a temporary basis?
Registration is done at permanent residence. To what is indicated in the passport. But you can send documents by mail. By law, it is possible to register an individual entrepreneur at the address of temporary registration at the place of residence, ONLY if there is no permanent residence permit in the passport (provided that it is more than six months old). You can conduct business in any city of the Russian Federation, regardless of the place of registration.
Can an individual entrepreneur register himself for work and make an entry in the labor himself?
An entrepreneur is not considered an employee and does not make any entries in his employment record. Theoretically, he can apply for a job himself, but this is his personal decision. Then he himself must conclude an employment contract with himself, make an entry in the work book and pay deductions, as for an employee. It's unprofitable and makes no sense.
Can an IP have a name?
An entrepreneur can choose any name for free, which would not directly conflict with the registered one - for example, Adidas, Sberbank, etc. In the documents and in the plate on the door, there should still be an IP full name. He can also register a name (register a trademark): it costs more than 30 tr.
Is it possible to work?
Can. At what you can not report at work that you have your own business. It does not affect taxes and fees in any way. Taxes and fees of the FIU must be paid - both as an individual entrepreneur and as a mercenary, in full.
Is it possible to register two sole proprietorships?
IP is just the status of an individual. It is impossible to become an IP twice at the same time (get this status if it already exists). TIN is always the same.
What are the perks?
There are no business benefits for the disabled and other privileged categories.
Some commercial organizations also offer their discounts and promotions. Online accounting Elba for newly created IP is now the first year as a gift (free of charge).
In order to make a profit from their work and at the same time remain clean before the state, an individual, according to the legislation of the Russian Federation, registers with state bodies either by creating an enterprise or by obtaining the status of an individual entrepreneur. This procedure is established by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and the Federal Law "On State Registration of Legal Entities and Individual Entrepreneurs". Making a profit without going through such procedures will lead to the imposition of penalties and other sanctions.
What individual entrepreneurship considered in detail in the legislative acts of the Russian Federation.
An individual entrepreneur is an individual who conducts business and has passed state registration in the manner prescribed by law without forming a legal entity.
From the moment the registration forms are received, the work carried out by an individual entrepreneur for the purpose of making a profit is regulated by the same parts of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation as for legal entities, however, the processes of work and interaction with counterparties and other market participants are simplified.
Aspects of Entrepreneurship:
As in any business, running a business as an individual entrepreneur has its advantages and disadvantages.
Positive sides from passing the procedure of state registration of IP:
Despite the positive aspects, an entrepreneur is the same responsible status as the founder has when creating a legal entity.
But on some positive aspects everything does not end, there are also disadvantages, which rarely anyone thinks about at the beginning of activity.

Despite all the nuances of being an individual entrepreneur, this is the only legal way to do business without organizing an enterprise.
When filing and compiling tax reports without violating the deadlines, maintaining accounting and engaging in legal activities, there will be no problems with government agencies.
Everything that passes through the organs state power always supported by legislative acts, the concept and activities of individual entrepreneurs are no exception.
The main laws and codes that a novice businessman is guided by in his activities:

The activity of an individual entrepreneur, despite the simplicity in comparison with legal entities, still imposes on an individual a lot of responsibilities in accordance with the specified regulations Russian legislation.
Some activities are subject to additional regulations, information about what other laws you need to study the entrepreneur receives when choosing his OKVED code.
Each entrepreneur is an independent person, and he has the right to choose the taxation system, based on his own convictions, and, if necessary, voluntarily change it in the manner prescribed by law.
Change tax regime for individual entrepreneurs, it can happen automatically due to exceeding the norms allowed by the current regime.

In total, the tax code defines 5 modes under which an individual entrepreneur can work:
Individual entrepreneurs have the right to apply several forms of taxation simultaneously, under certain types activities. This allows you not to exceed the limits established by law on the simplified tax system and the patent, and to avoid restrictions on doing one or another type of business.
 Due to the fact that individual entrepreneurship is a simplified form of state registration of a business, it has a number of limitations. May be applicable to all entrepreneurs or depending on the chosen taxation system.
Due to the fact that individual entrepreneurship is a simplified form of state registration of a business, it has a number of limitations. May be applicable to all entrepreneurs or depending on the chosen taxation system.
OKVED involves the division of all types of activities into 4 groups:
Prohibited activities that, regardless of the form of taxation, individual entrepreneurs cannot engage in:

You will need to obtain a license before starting work for the following activities:
Depending on the form of taxation, restrictions on work may also be imposed.
Table 1. Restrictions on the activities of individual entrepreneurs based on the tax base chosen during registration
| Limitation | BASIC | USN | UTII* | Patent |
| State | Without Borders | Up to 100 people | No more than 100 | Up to 10 people |
| Annual turnover, rub. | Not installed | 150 million | Not | 60 million |
| Everything is allowed, except for those prohibited by the state for individual entrepreneurs | It is not allowed to establish companies providing services legal services, pawnshops and gambling business. | Can be used only for activities defined in paragraph 2 of Art. 346.26 ch. 26.3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation | Everything is prohibited, except for those provided for in paragraph 2 of Art. 346 of Chapter 26.4 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as patent activities. |
* According to UTII in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, there are a number of additional restrictions, among them the size of retail premises should not exceed 150 sq. m, the number of cars in the fleet for individual entrepreneurs providing transportation services cannot exceed 20 units.
It is preferable for an individual entrepreneur to decide on the types of activity and form of taxation before passing state registration. Restrictions on certain OKVED will not allow you to operate within the law and obtain the necessary certificates, and for violation of these parts of the law, criminal liability is provided.
If everything is decided with the types of activities and the form of taxation, then the entrepreneur must undergo the procedure of mandatory state registration, for this, the following are submitted to the registration authority:
 Within 5 days after the submission of a complete package of papers, if the entrepreneur has no claims from state bodies, he receives a certificate of state registration, and information about it is entered in the register, where all data about the individual entrepreneur will be stored until the termination of activity.
Within 5 days after the submission of a complete package of papers, if the entrepreneur has no claims from state bodies, he receives a certificate of state registration, and information about it is entered in the register, where all data about the individual entrepreneur will be stored until the termination of activity.
An individual, regardless of citizenship, who has reached the age of majority and is recognized as capable can become an individual entrepreneur. For foreigners, it is mandatory to have documents confirming legal grounds to stay on the territory of the Russian Federation (RVP or a view of permanent place residence).
In some cases, IP status can be obtained by persons under the age of 18 if they are recognized by the authorized bodies as adults ahead of schedule, as a result of marriage or with permission from their parents or other legal representatives (guardians).
Individual entrepreneurs, as well as legal entities, have the right to use the labor of hired workers. In order to get a legal opportunity to hire people to perform work, an individual entrepreneur (the requirements were in effect until 2017) must go through the registration procedure as an employer in pension fund, FFOMS and FSS, having received the relevant certificates.
Since 2017, an individual entrepreneur is only obliged, upon employment of the first employee, to submit to the FSS information that he has begun an employment relationship with an individual. This must be done within the time limits established by law - 30 calendar days. Otherwise, fines are provided for 90 days of delay - 5,000 rubles, over - 10,000 rubles.
 The sequence of actions for registering an employee for an individual entrepreneur does not differ much from the standard procedure for enterprises of other forms of ownership:
The sequence of actions for registering an employee for an individual entrepreneur does not differ much from the standard procedure for enterprises of other forms of ownership:
Accept a package of documents from the future employee, which includes:
If an individual has not previously been employed, registration of SNILS and work book is an obligation of the individual entrepreneur, as the first employer for such an employee:
If the employee has not worked for 5 days and quit, you can not make an entry in the labor force.
In cases where an individual entrepreneur decides to end his business activities, he must close the IP in accordance with the procedure established by law. The procedure for termination of entrepreneurship, as well as registration, is regulated by the Federal Law “On State Registration of Legal Entities and Individual Entrepreneurs”. The procedure is determined by Art. 22.3 of the said act. In cases of forced termination of activity or death of an individual entrepreneur, registration authorities are guided by the data received from public institutions, courts or notaries.
As for the voluntary order, the individual entrepreneur must submit the following documents to the structures:
Before formalization termination of business activities, an individual retains the obligation to pay taxes and fees prescribed by law, regardless of whether the business is conducted or not, therefore, it should be borne in mind that such completion of work is unacceptable for the individual entrepreneur himself.
Conducting activities and receiving financial benefits from it in Russia without going through state registration procedures is an illegal form of earnings. At the same time, the formation of an enterprise is a complex and lengthy process. If the view economic activity allows, then most individuals choose to register as an individual entrepreneur. The opportunities obtained in this case are slightly less than those of legal entities, and there are no claims from the authorities and law enforcement agencies.