So, your goal is to insulate the house. Let's assume that the stage of material selection has already been passed, and the scales have tipped towards stone wool insulation, which is environmentally friendly, safe, good vapor permeability and incombustibility, combined with excellent thermal performance.
And then one of the most burning questions appears: “How to choose the thickness of the insulation?” In this article, we will focus specifically on determining the required thickness using the example of stone wool insulation. The calculation method is based on an algorithm used by professional builders and designers for various building designs.
The methodology itself and all reference data are in several regulatory documents, which today are called SP - set of rules. This is SP 50.13330.2012 (formerly SNiP 23-02-2003) "Thermal protection of buildings" and a collection of tables - SP 131.13330.2012 (formerly SNiP 23-01-99 *) "Construction climatology".
For residential buildings in the north of our country, more insulation is needed than by the warm sea. How severe the winter in a particular region can be determined based on the duration of the heating period (in days) and the average temperature during this time. The period of "hot batteries" for residential buildings begins when the average daily air temperature drops below +8°C. All these data are contained in the "Construction Climatology". So, for Moscow, the heating period lasts 214 days, and the average temperature at this time is -3.1°C.

In calculating the thickness of the insulation, climate parameters are taken into account based on indicators under the abbreviation GSOP (degree-day of the heating period). It shows how many degrees and for how many days it is necessary to raise the temperature outside the window to a comfortable + 20 ° C inside the house with the help of heating. It is calculated as the difference between the internal temperature (+20°C) and the average for the heating period, multiplied by the duration of this period in days.
In SP 50.13330.2012 there is a table that, depending on the GSOP, allows you to determine the required thermal resistance for roof or wall. This indicator illustrates how effectively a roof or wall must resist heat transfer, which is why it has such a name.
The thermal resistance of a finished structure, such as a wall, is the sum of the resistances of each of the layers, which is equal to the thickness of the layer in meters divided by its coefficient of thermal conductivity"lambda" - λ. That is why the lower the thermal conductivity coefficient, the more reliably the material retains heat with a smaller thickness of its layer. By selecting the thickness of the insulation, it is ensured that the total resistance to heat transfer of the structure is greater than required.
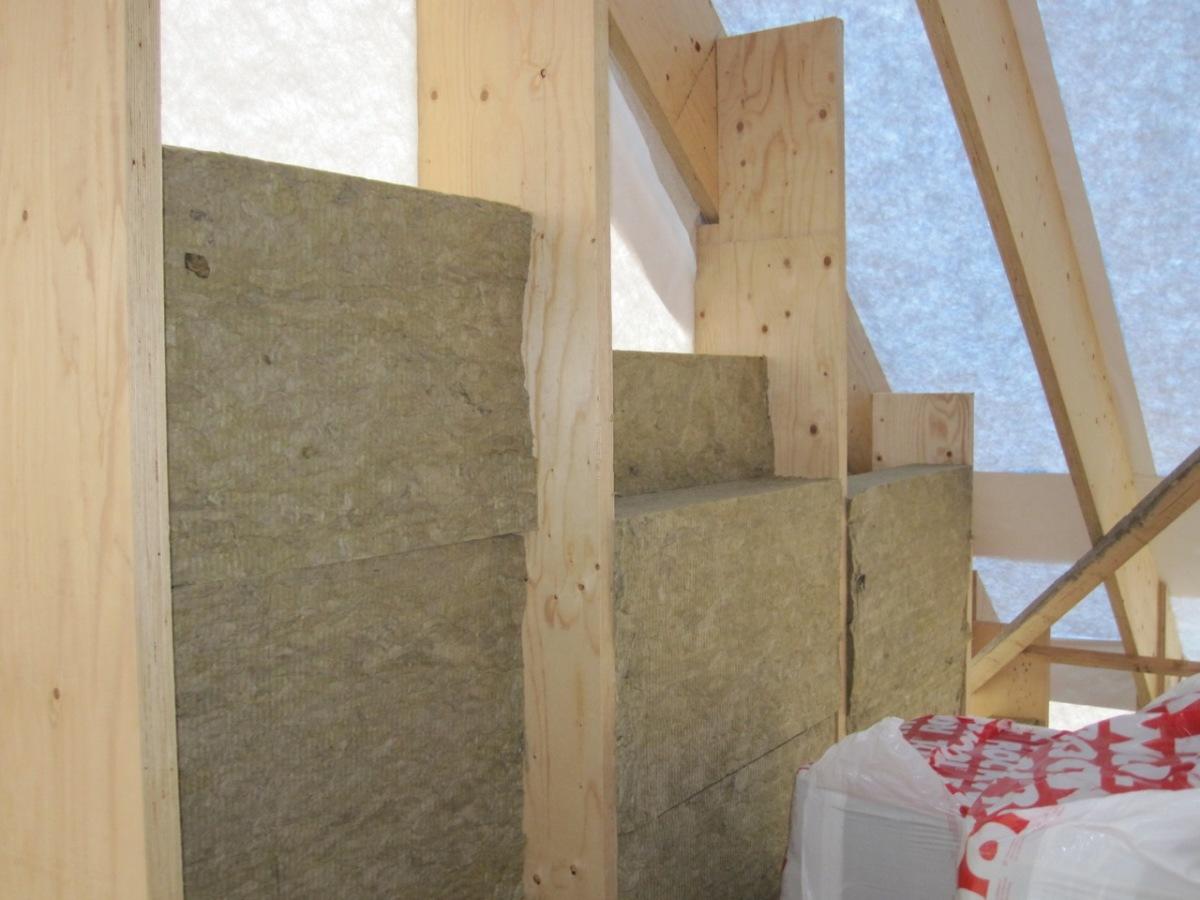

For example, if you use an effective stone wool material ROCKWOOL LIGHT BUTTS SCANDIC, which has an extremely low thermal conductivity (λA, λB - 0.039 and 0.041 W / (m²x ° C)) and has no analogues on the market, then it is at a smaller thickness than others heaters, allows you to achieve the desired effect.
The calculation does not use the coefficient of thermal conductivity with indices 10 or 25 (λ10, λ25), since these are laboratory indicators of a completely dry material, and this does not happen in a real design. In all dry regions of our country, λA values are taken for calculations, and for regions with a humid and normal regime, which are the majority in Russia, λB is used, where A and B are the operating conditions of building structures in terms of humidity.
With a certain degree of skepticism, one should perceive information about materials whose manufacturer or seller claims a thermal conductivity coefficient of less than 0.025 W / (m²x ° C). Air at +20°C has this coefficient. It is he, divided by the structure of the material into small portions, that makes the greatest contribution to the resistance to heat transfer. Therefore, until scientists have learned to “pour vacuum into tanks”, this is an unattainable value of thermal conductivity, which all heaters in construction strive for.
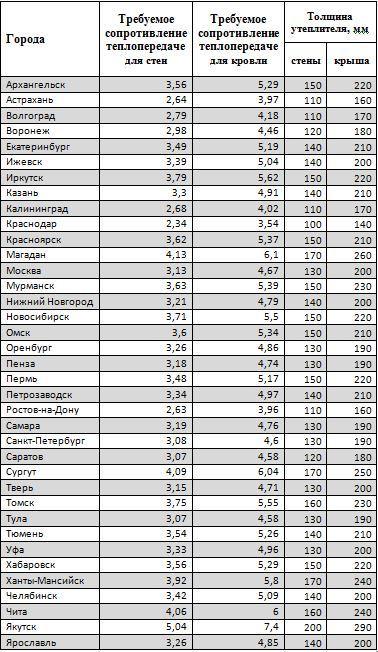
The values of the required thermal resistance for frame roofs and walls of residential buildings in some Russian cities are shown in the table below. There is also a minimum thickness of insulation that will be sufficient to meet the requirements for heat transfer (for example, the material of the company ROCKWOOL LIGHT BATTS SCANDIC is taken).
The house is not built for one day, so the question of the reliability of the insulation naturally arises. It is best to use materials from companies that have been manufacturing their products for a long time and are successfully operating in the market. Such manufacturers not only have information on the real durability of their materials, but also set themselves the task of constantly improving the characteristics of products and the technology of their manufacture and installation.
LIGHT BATTS SCANDIC is a universal insulation for non-load-bearing frame structures, which are most often found in private houses, for example, for walls, floors along logs and attics. This product is a new generation of the well-known and well-proven LIGHT BATTS insulation. Retaining the density and thermal characteristics of its predecessor, it has acquired a revolutionary quality of stone wool fibers, which allows the plates to be subjected to compression (compression) up to 60%. Thanks to this, its delivery is almost three times more profitable.
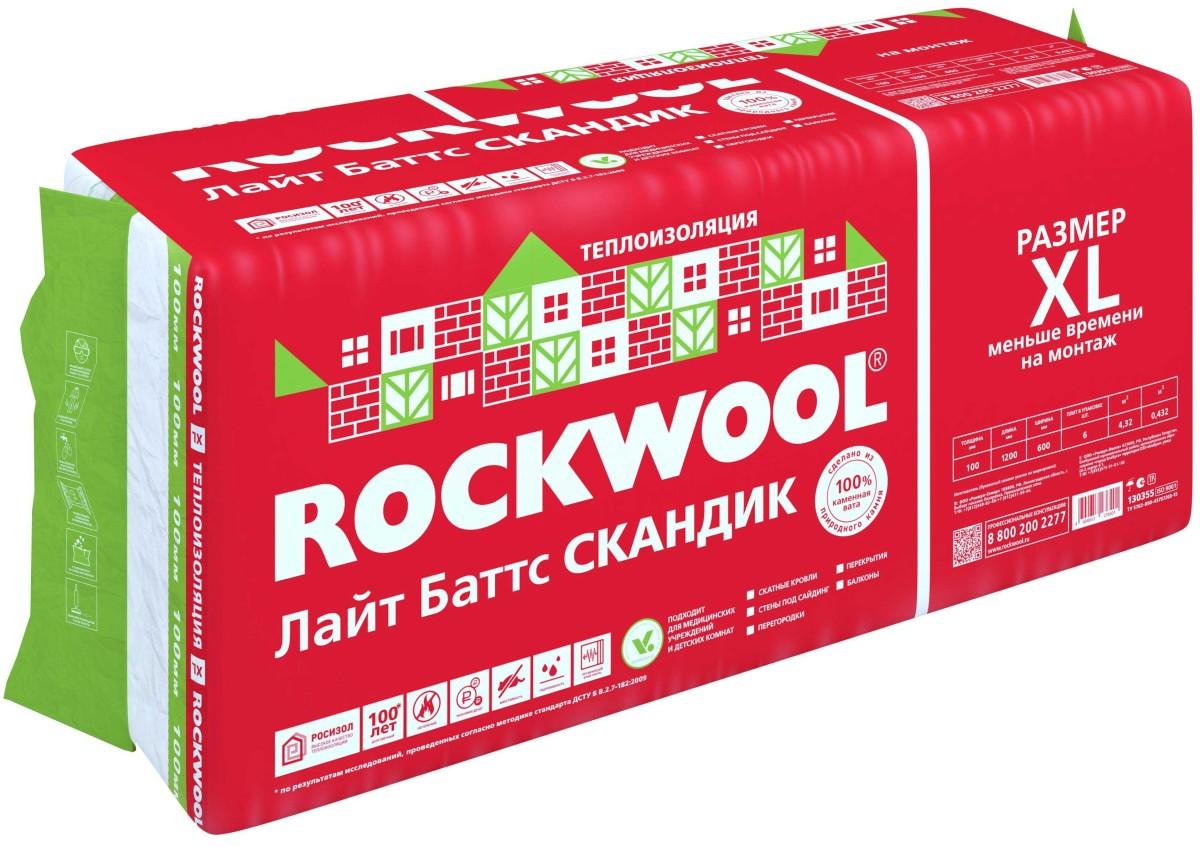

The thermal resistance of only 100 mm of LIGHT BUTTS SCANDIC insulation (λB=0.041 W/(m²x°C)) will be equal to 2.44 (m²x°C)/W. Such resistance can be provided by a wall of almost two meters thick made of solid ceramic (red) bricks (λB=0.81 W/(m²x°C)). Obviously, 200 mm of the same insulation creates a thermal resistance of the layer twice as much - 4.88 (m²x ° C) / W.
To insulate a private frame house, the insulation layer should be made of a material with a thickness of at least 100 mm. So, for frame walls, floors along logs and an insulated attic of a house in the Moscow region, 200 mm of insulation for the roof, 150 mm for walls and 200 mm for the floor will be enough.
Calculating the thickness of thermal insulation, even if greatly simplified, requires both time and effort, but there is a way out, and it is quite simple. On the website of the Russian division of the company, you can find and freely download brochures with installation recommendations, as well as the necessary certificates for products and systems.
In the "Video Library" subsection, as well as on the ROCKWOOL YouTube channel, tutorial videos on installation are posted. On the main page of the site there is a convenient one that allows you to quickly and easily select the thickness of the thermal insulation based on the normative calculation, calculate the amount of material and evaluate the financial savings from using a thicker layer of insulation.
Today, professional home insulation is a task that everyone can do. ROCKWOOL is always ready to help you find the necessary information and talk about the features of the installation of certain structures. By putting into practice the advice of experts, you can professionally insulate your home, making it warm, cozy and safe for many years.
